Abdominal muscles
What is Gilmore’s Groin?
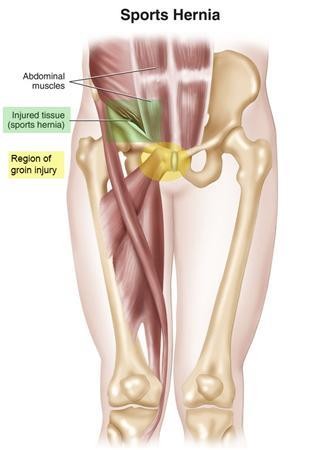
Gilmore’s Groin, also known as sports hernia or athletic pubalgia is a syndrome that occurs in professional athletes or people that exercise intensively (a number of hours a day). The pain is caused by the posterior abdominal wall muscles being weakened. As a result the opening in the inguinal canal widens and a hernia (protrusion) may occur. The pain is brought on by explosive movements and often occurs in sports that involve many short, explosive movements, such as in football, hockey, rugby, basketball etc. This condition manifests in pain in the groin that increases as a result of exercise. Exercises in which intra-abdominal pressure increases, such as when performing sit-ups, may aggravate the pain. This condition is more common in men than in women.
Treatment for Gilmore’s Groin
Treatment for Gilmore’s groin or a sports hernia will first begin with a conservative policy. Exercise is halted for between six and eight weeks, an anti-inflammatory is taken and physiotherapy must be followed. The physiotherapy focuses primarily on core-stability exercises, stability exercises for the pelvis and general flexibility training. Sudden, explosive rotating movements must be avoided during this period or the recovery period will be longer. If the conservative approach fails, surgical intervention can be considered in which the weakened abdominal wall is repaired and strengthened in a hernia operation. This is possible via keyhole or open surgery.
This content was written by : Dr. Yves Devlies, Dr. Pieter-Jan De Roo, Dr. Paul Gunst, Dr. Jan Noyez, Dr. Luc Van den Daelen, Dr. Jan Van Oost, Dr. Philip Winnock de Grave