Shoulder prosthesis, types of prosthesis and the rehabilitation after the operation
Introduction
With the prospect of pain relief, in combination with restoring the arm function, increasing the self-sufficiency as a result.
In this respect a shoulder replacement can be a very fulfilling surgery, primarily for the patient as well as for the surgeon.
The intention of the brochure is to adjust the discredit towards shoulder replacement in order to inform and reassure the patient.
Types of shoulder prostheses:
Shoulder replacement has become much more popular in the past 20 years. Earlier this type of surgery wasn’t entirely accurate and had a negative connotation for reasons of pain and permanent limitation of the shoulder function. These prejudices were nevertheless mainly false. The experiences and results with shoulder prostheses have improved over the past 20 years. This type of surgery results in loss of pain as well as rehabilitation of the arm function which enhances the self-sufficiency. A shoulder replacement can therefore be a very fulfilling surgery, primarily for the patient as well as for the surgeon.
There are 3 main reasons why to consider shoulder replacement.
When we’re dealing with an irreversible tear of several tendons around the shoulder. This is most common . In this case we choose to replace the shoulder with a ‘reversed’ prosthesis (rotator cuff deficient prosthesis).
In rare cases there is severe cartilage deteriotation, arthrosis, but where the tendons are undamaged. The best option here is to replace the shoulder by means of an anatomical prosthesis.
A complex shoulder fracture, where the shoulder is too damaged, can be another reason to replace it In this case the ball of the shoulder should be replaced by a new ball and therefore is called a fracture-prothesis or hemi-prosthesis.
The reversed shoulder prosthesis
Definition
Most common type of wear around the shoulder is cartilage wear. At young age tendon structures are still strong. The tendons may tear as a result of spontaneous ageing processes, which is a common process. If possible, the tear should be surgically treated.
Over the age of 70 we are often confronted with irreversible tendon damage which causes damage of the shoulder joint and reduced arm strength.
In this case the best solution is to replace the shoulder by means of a reversed shoulder prosthesis.
Paul Grammont is the founder of the reversed shoulder prosthesis. He defined that on the glenoid a head should be placed and at the same time the humeral head should be replaced by a cup. This particular technique makes it possible for intact tendons to function better and as a substitute for the torn and damaged tendons.
Diagnosis
Mostly it involves an elderly patient who has chronic, continuing pain in the shoulder and upper arm combined with reduced function and strength. In some cases it can jeopardise self-sufficiency when the patient has difficulty dressing or undressing, brushing his teeth or even eating.
A torn tendon can cause excruciating pain, restricted movement of the arm, particularly above the horizontal plane, and reduced strength.
The ultra sound examination can show wear or rupture of the tendons.
As a consequence of this wear, the ultra sound shows characteristics of a degenerative process, mostly an elevated humeral head.

We proceed to reversed shoulder replacement surgery if at least 2 tendon structures are irreversibly damaged.
Treatment
Prior to the operation the anesthesiologist will administer local anestheasia, an injection in the neck, to sedate the nerves from the neck to the shoulder. This will reduce the pain after the operation.
An anterior incision in the shoulder will enable the surgeon to cut the capsule between the arm- and chest muscle. The humeral head will be dislocated.
Next step is progressive reaming of the medullar canal of the humerus. With a specific aiming device only a minimal amount of bone will be resected.
Next is providing an opening in the shoulder cup in order to insert the handle of the base plate.

With the use of several screws the humeral head will be attached to that plate.


Finally the prosthesis will be inserted in the medullar canal on which the cup will be attached.


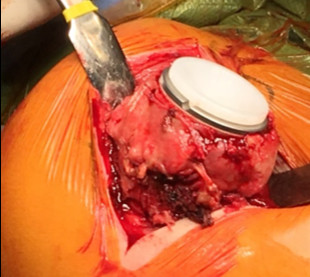
The shoulder will be put back into place. After a stability check-up, the wound will be closed.

Rehabilitation
Contrary to what many people believe and fear, the follow-up treatment is in fact very simple and immobilization of the shoulder is unnecessary.
It is recommended to wear the shoulder sling only at night, for 2 weeks.
The full recovery period will take 3 to 4 months, where after 2 weeks you are already self-sufficient.
The anatomical shoulder prosthesis
Definition
Unlike the hip or the knee, the shoulder doesn’t have to support your body weight. Therefore sheer wear, arthrosis, of the shoulder is rare.
In case of pure arthrosis the damaged head and cup will be replaced by a prosthesis made of steel and poly-ethylene.
Diagnosis
Once again it involves continuing, long-term, often over night shoulder pain, progressively affecting the ability to function.
The ultra sound however shows a well preserved rotator cuff which therefore gives us no arguments for a tear.
A standard ultra sound most likely shows wear very clearly, in the shape of a parrot’s beak.

Often a collapse of the head can be noticed due to osteo necrosis. During surgery we see that the cup is well preserved but the underlying bone tissue is dead.


These are indications to replace the shoulder by an anatomical prosthesis.

Treatment
The surgery is similar to that of a reversed shoulder replacement. Once the opening has been made in the cup, it is covered in a poly-ethylene manufactured flat cup.
Afterwards the prosthesis is put into the medullar canal, where a metal head is attached onto, which approximates the size of the original head.


Finally the anterior joint capsule structures are being closed.
Follow-up treatment
This surgery quickly allows the patient to actively and passively mobilize the shoulder, with just a few restrictions according to which technique has been used.
The fracture-shoulder prothesis
Definition
A fall on to the shoulder (most likely while cycling) is a common occurrence. A shoulder reconstruction using osteosynthesis will be proposed if possible and certainly in case of younger patients. In case of elderly patients these fractures are much more complex, taking into account the patient’s bone quality and functioning of the shoulder before the accident, which makes it impossible to use osteosynthesis.
The best solution in this case is to replace the shoulder by a fracture-shoulder prosthesis.
Depending on the patient’s age and quality of the surrounding tendons, an anatomical fracture-prosthesis will be used. However, it concerns often eldery patients (where wear is already present) which makes a reversed fracture-prosthesis the best option.
Diagnosis
Patients who are forced to the emergency room with excruciating pain and loss of function in the affected shoulder and arm due to a fall.

The ultra sound examination indicates the fracture. Besides the fracture of the head of the shoulder, we often see that 1 or 2 bony projections on the upper side of the upper bone are broken. These projections are important because several tendons, which are essential for the shoulder to function proper, are attached. If possible these fractures should be repaired as well during surgery.
Treatment
The numerous bone fragments with the attached tendons have to be located first. The humeral head will be removed and replaced by an artificial head.


A reversed or anatomical prosthesis will replace the shoulder.


Finally the loose bone fragments and its attached tendons will be restrained to the prosthesis.
This part is obviously the hardest but yet most important step of the entire operation.

Rehabilitation
If the fractured projections had to be repaired during surgery, it will take 6 to 8 weeks to regenerate on to the prosthesis. Therefore the rehabilitation will be slower because active exercises aren’t allowed during the healing period. After this 6 to 8 week period the active training sessions can get started. The full recovery will take about 4 to 6 months, counting on full gain of function.
This content was written by : Dr. Yves Devlies, Dr. Stijn Muermans, Dr. Peter Stuer, Dr. Alexander Ryckaert, Dr. Karel Willems